Link types
The Multidoc navigation system is based on HTML link types. The link type is what goes in the rel or rev attribute of an HTML anchor or link tag. For now, Multidoc only understands rel. (rev is not so useful, and indeed is hardly used these days.)
The HTML specification lists “recognized link types” (see above link), although it also allows authors to define their own link types. While I think it is a good idea to largely stick to the recognized types, Multidoc allows you to name your link types anything you want. If you want to have a FUBAR link type, you can:
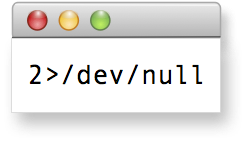
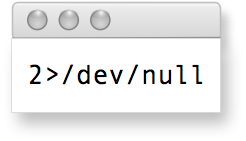
<txp:soo_multidoc_link rel="FUBAR" />
I really did use the above markup to produce this link: if you look at the page source you’ll see the anchor tag picked up the rel attribute. The point of this very silly example is to show that you can indeed make up your own link types. However, Multidoc does have a few:
Reserved type names
The link type names Start, Up, Next, and Prev have special meaning in Multidoc. You can, and almost certainly will, use these type names in the rel attribute of the soo_multidoc_link tag, but do not assign these types to pages within your collections. Multidoc automatically finds these links for you.
Page order: Next & Prev
In a linear collection, Next and Prev work as you would expect. How about in a hierarchical collection? Multidoc determines page order by a depth-first traversal, that is, in the same order you would expect from a table of contents.
Combining link types
The rel attribute of an anchor or link tag is allowed to contain multiple HTML link types, each type separated by a space. Multidoc understands only two such combinations: Next or Prev followed by a document type such as Page or Section. For example:
<txp:soo_multidoc_link rel="next section" add_title="1" />
takes you to the top page of the next section in this collection: Tag reference
Posted 2009-01-26 (last modified 2010-09-12)